FUTURE LIFE The immortality of the soul and the reality of a future life are very distinctive doctrines of the religion of Muhammad, and very numerous are the references to it in the Qur'an. The whole system of Islam is based upon the belief in the future existence of the soul of man. A description of the special character of this future life will be found in the article on PARADISE.
The terms generally used to express a future life are Daru 'l Akhirat, Daru 'l-Baqa, Daru 'l-Uqba.
Hughes' Dictionary of Islam
Answering Islam Home Page
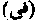 Booty obtained from infidels. According to Muhammad ibn Tahir, fai' is booty taken from a country which submits to Islam without resistence, as distinguished from ghanimah, or plunder. The Khalifah 'Umar said it was the special privilege of the Prophet to take booty as well as plunder, a privilege not permitted to any other prophet.
Booty obtained from infidels. According to Muhammad ibn Tahir, fai' is booty taken from a country which submits to Islam without resistence, as distinguished from ghanimah, or plunder. The Khalifah 'Umar said it was the special privilege of the Prophet to take booty as well as plunder, a privilege not permitted to any other prophet.
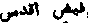 , Persian) Communications of divine grace made to angels and prophets and other superior intelligences.
, Persian) Communications of divine grace made to angels and prophets and other superior intelligences.
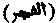 "The Daybreak." The title of the lxxxixth Surah of the Qur'an, in the first verse of which the word occurs.
"The Daybreak." The title of the lxxxixth Surah of the Qur'an, in the first verse of which the word occurs.
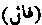 . A good omen, as distinguished from tiyarah, "a bad omen".
. A good omen, as distinguished from tiyarah, "a bad omen".
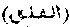 "The Daybreak." The title of the cxiiithe Surah of the Qur'an. The word signifies cleaving, and denotes the breaking forth of the light from the darkness.
"The Daybreak." The title of the cxiiithe Surah of the Qur'an. The word signifies cleaving, and denotes the breaking forth of the light from the darkness.
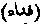 Extinction. The last stage in the Sufiistic journey. [SUFIISM.]
Extinction. The last stage in the Sufiistic journey. [SUFIISM.]
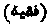 . A Muhammadan lawyer or theologian. The term is still retained in Spanish as alfaqui. [FIQH.]
. A Muhammadan lawyer or theologian. The term is still retained in Spanish as alfaqui. [FIQH.]
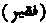 . Persian darwesh. The Arabic word faqir signifies "poor"; but it is used in the sense of being in need of mercy, and poor in the sight of God, rather than in need of worldly assistance. Darwesh is a Persian word, derived from dar, "a door", ie those who beg from door to door. The terms are generally used for those who lead a religious life. Religious faqirs are divided into two great classes, the ba shar' (with the law), or those who govern their conduct according to the principles of Islam;
. Persian darwesh. The Arabic word faqir signifies "poor"; but it is used in the sense of being in need of mercy, and poor in the sight of God, rather than in need of worldly assistance. Darwesh is a Persian word, derived from dar, "a door", ie those who beg from door to door. The terms are generally used for those who lead a religious life. Religious faqirs are divided into two great classes, the ba shar' (with the law), or those who govern their conduct according to the principles of Islam;





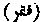 The life of a Faqir or an ascetic.
The life of a Faqir or an ascetic.
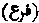 The first born of either camels, sheep, or goats, which the Arab pagans used to offer to idols. This was allowed by the Prophet at the commencement of his mission, but afterwards abolished. (Mishkat, book iv c 50.)
The first born of either camels, sheep, or goats, which the Arab pagans used to offer to idols. This was allowed by the Prophet at the commencement of his mission, but afterwards abolished. (Mishkat, book iv c 50.)
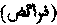 pl. of Farizah. "Inheritances". A term used for the law of inheritance, or 'Ilmu 'l-Fara'iz. Farizah means literally an ordination of God, and this branch of Muslim law is so called because it is established fully in the Quran, Surah iv. [INHERITANCE.]
pl. of Farizah. "Inheritances". A term used for the law of inheritance, or 'Ilmu 'l-Fara'iz. Farizah means literally an ordination of God, and this branch of Muslim law is so called because it is established fully in the Quran, Surah iv. [INHERITANCE.]
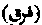 lit. "Separation". Faraq-I Awwal is a term used by Sufi mystics to express that state of mind in which the soul is drawn away from a contemplation of God by a contemplation of his creation; and furaq-I-sani (the second separation) is when the soul is constantly contemplating the stability of the creation with the eternity of the Creator. ('Abdu 'r-Razzaq's Dictionary of Sufi Terms.)
lit. "Separation". Faraq-I Awwal is a term used by Sufi mystics to express that state of mind in which the soul is drawn away from a contemplation of God by a contemplation of his creation; and furaq-I-sani (the second separation) is when the soul is constantly contemplating the stability of the creation with the eternity of the Creator. ('Abdu 'r-Razzaq's Dictionary of Sufi Terms.)
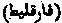 The Arabic rendering of the Greek
The Arabic rendering of the Greek 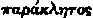 , "Paraclete." Muhammadan writers assert that it is the original of the word translated Ahmad in the following verse in the Qur'an, Surah lxi v 6:-
, "Paraclete." Muhammadan writers assert that it is the original of the word translated Ahmad in the following verse in the Qur'an, Surah lxi v 6:-
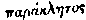 may, have been rendered
may, have been rendered 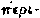
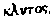 , which in some early Arabic translation of the Gospel may have been translated Ahmad. In the Maja'u 'l-Bihar, a work written three hundred years ago, the word faraqlit is said to mean a distinguisher between truth and error. The word also occurs several times in the well-known Shia'ah work, the Hayatu 'l-Qulub (vide. Merrick's translation, page 86). The author syas, "It is well known that his (the Prophet's) name in the Taurat is Muadmund, in the Gospels (Injil) Tabtab, and in the Psalms (Zabur) Farakleet." And again (p. 308), "God said to Jesus, son of my handmaid....verily, I will send the chosen of prophets, Ahmad, whom I have selected of all my creatures even Faraleet, my friend and servant." [JESUS.]
, which in some early Arabic translation of the Gospel may have been translated Ahmad. In the Maja'u 'l-Bihar, a work written three hundred years ago, the word faraqlit is said to mean a distinguisher between truth and error. The word also occurs several times in the well-known Shia'ah work, the Hayatu 'l-Qulub (vide. Merrick's translation, page 86). The author syas, "It is well known that his (the Prophet's) name in the Taurat is Muadmund, in the Gospels (Injil) Tabtab, and in the Psalms (Zabur) Farakleet." And again (p. 308), "God said to Jesus, son of my handmaid....verily, I will send the chosen of prophets, Ahmad, whom I have selected of all my creatures even Faraleet, my friend and servant." [JESUS.]
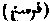 Persian Farsany. A land measure which occurs in Muhammadan books of law. It is a league of 18,000 feet, or three and a half miles in length.
Persian Farsany. A land measure which occurs in Muhammadan books of law. It is a league of 18,000 feet, or three and a half miles in length.
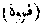 An Arab of the Banu Juzam and Governor of 'Amman, who is represented by tradition (upon imperfect evidence) as one of the early martyrs of Islam. Having been converted to Islam, the Roman authorities crucified him (Muir's Life of Mahomet, vol. ii, p 103.)
An Arab of the Banu Juzam and Governor of 'Amman, who is represented by tradition (upon imperfect evidence) as one of the early martyrs of Islam. Having been converted to Islam, the Roman authorities crucified him (Muir's Life of Mahomet, vol. ii, p 103.)
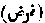 That which is obligatory. A term used for those rules and ordinances of religion which are said to have been established and enjoined by God Himself, as distinguished from those which are established upon the precept or practice pf the Prophet, and which are called sunnah.
That which is obligatory. A term used for those rules and ordinances of religion which are said to have been established and enjoined by God Himself, as distinguished from those which are established upon the precept or practice pf the Prophet, and which are called sunnah.
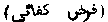 A command which is imperative (jarz) upon all Muslims, but which if one person in eight or ten performs it, it is sufficient (kifa'i), or equivalent to all having performed it.
A command which is imperative (jarz) upon all Muslims, but which if one person in eight or ten performs it, it is sufficient (kifa'i), or equivalent to all having performed it.
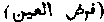 . An injunction or ordinance the obligation of which extends to every Muslin, as prayer, fasting, &c.
. An injunction or ordinance the obligation of which extends to every Muslin, as prayer, fasting, &c.
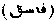 . A seditious or rebellious person.
. A seditious or rebellious person.
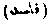 . A term used in Muhammadan law for a reprobate person who neglects decorum in his dress and behavior. The acceptance of such a person's evidence is not admissible. He is not regarded as a Muslim citizen, although he may profess Islam.
. A term used in Muhammadan law for a reprobate person who neglects decorum in his dress and behavior. The acceptance of such a person's evidence is not admissible. He is not regarded as a Muslim citizen, although he may profess Islam.
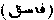 Persian Rozah
Persian Rozah 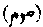 . Fasting was highly commended by Muhammad as an atonement for sin. The following are the fasts founded upon the example of the Prophet and observed by devout Muslims:-
. Fasting was highly commended by Muhammad as an atonement for sin. The following are the fasts founded upon the example of the Prophet and observed by devout Muslims:-
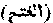 "The Victory". The title of the XLVIIIth Surah of the Qur'an, in the first verse of which the word occurs, "Verily We (God) have given thee an obvious victory, that God may pardon thee thy former and later sin."
"The Victory". The title of the XLVIIIth Surah of the Qur'an, in the first verse of which the word occurs, "Verily We (God) have given thee an obvious victory, that God may pardon thee thy former and later sin."
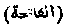 Lit. "The opening one." The first chapter of the Qur'an, called also the Suratu 'l-Hamd, or the Chapter of Praise." It is held in great veneration by Muhammadans, and is used by them very much as the Paternester is recited by Roman Catholics. It is repeated over sick persons as a means of healing and also recited as an intercession for the souls of the departed, and occurs in each rak'ah of the daily prayer. Muhammad is related to have said it was the greatest Surah in the Qur'an and to have called it the Qur'anu 'l-Azim, or the "exalted reading." It is also entitle the Sab'u 'l-Masam, or the "seven recitals", as it contains seven verses; also Ummu 'l-Qur'an, the "Mother of the Qur'an." According to a saying of the Prophet, the fatihah was revealed twice, once at Makkah and once at al-Madinah. The Amin always said at the conclusion of this prayer.
Lit. "The opening one." The first chapter of the Qur'an, called also the Suratu 'l-Hamd, or the Chapter of Praise." It is held in great veneration by Muhammadans, and is used by them very much as the Paternester is recited by Roman Catholics. It is repeated over sick persons as a means of healing and also recited as an intercession for the souls of the departed, and occurs in each rak'ah of the daily prayer. Muhammad is related to have said it was the greatest Surah in the Qur'an and to have called it the Qur'anu 'l-Azim, or the "exalted reading." It is also entitle the Sab'u 'l-Masam, or the "seven recitals", as it contains seven verses; also Ummu 'l-Qur'an, the "Mother of the Qur'an." According to a saying of the Prophet, the fatihah was revealed twice, once at Makkah and once at al-Madinah. The Amin always said at the conclusion of this prayer.
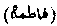 A daughter of Muhammad, by his first wife Khadijah. She married 'Ali the cousin of Muhammad, by she had three sons, al-Hasan, al-Husain, and al-Muhsin; the latter died in infancy. From the two former are descended the posterity of the Prophet known as Saiyids. Fatimah died six months after her father. She is spoken of by the Prophet as one of the four perfect women, and is called al-Batul, or "the Virgin", by which is meant one who had renounced the World, also Fatimatu 'z-zubra, or "the beautiful Fatima."
A daughter of Muhammad, by his first wife Khadijah. She married 'Ali the cousin of Muhammad, by she had three sons, al-Hasan, al-Husain, and al-Muhsin; the latter died in infancy. From the two former are descended the posterity of the Prophet known as Saiyids. Fatimah died six months after her father. She is spoken of by the Prophet as one of the four perfect women, and is called al-Batul, or "the Virgin", by which is meant one who had renounced the World, also Fatimatu 'z-zubra, or "the beautiful Fatima."
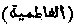 "The Fatimides". A dynasty of Khalifahs who reigned over Egypt and North Africa from A.D. 908 to A.D. 1171. They obtained the name from the pretensions of the founder of their dynasty Abu Muhammad 'Ubaidu'llah, who asserted that he was a Saivid, and descended from Fatimah, the daughter of the Prophet and 'Ali. His opponents declared he was the grandson of a Jew of the Magian religion.
"The Fatimides". A dynasty of Khalifahs who reigned over Egypt and North Africa from A.D. 908 to A.D. 1171. They obtained the name from the pretensions of the founder of their dynasty Abu Muhammad 'Ubaidu'llah, who asserted that he was a Saivid, and descended from Fatimah, the daughter of the Prophet and 'Ali. His opponents declared he was the grandson of a Jew of the Magian religion.
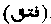 Lit. "Opening." A term used by Sufi mystics to explain the eternity of matter, together with its development in creation. ('Abdu 'r-Razzaq's Dict. of Sufi Terms.)
Lit. "Opening." A term used by Sufi mystics to explain the eternity of matter, together with its development in creation. ('Abdu 'r-Razzaq's Dict. of Sufi Terms.)
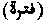 Lit. "Langour," or "Intermission". (1) The interval between the supposed revelation of the xcvith Surah of the Qur'an and the lxxivth and xciiird Surahs. It is during this period that the powers of inspiration of the Prophet are said to have been suspended, and it was then that he contemplated suicide by intending to cast himself from Mount Hira. The accounts of this interval are confused and contradictory, and various are the periods assigned to it, viz. from seven months to seven years.
Lit. "Langour," or "Intermission". (1) The interval between the supposed revelation of the xcvith Surah of the Qur'an and the lxxivth and xciiird Surahs. It is during this period that the powers of inspiration of the Prophet are said to have been suspended, and it was then that he contemplated suicide by intending to cast himself from Mount Hira. The accounts of this interval are confused and contradictory, and various are the periods assigned to it, viz. from seven months to seven years.
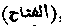 , "The Opener" of that which is difficult.
, "The Opener" of that which is difficult.
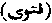 . A religious or judicial sentence pronounced by the Khalifah or by a Mufti, or Qazi. It is generally written. The following is a fatwa delivered by the present Mufti of the Hanafi sect at Makkah in reply to the question as to whether India is a Daru 'l-Islam. Fatwas are generally written in a similar form to this, but in Arabic:-
. A religious or judicial sentence pronounced by the Khalifah or by a Mufti, or Qazi. It is generally written. The following is a fatwa delivered by the present Mufti of the Hanafi sect at Makkah in reply to the question as to whether India is a Daru 'l-Islam. Fatwas are generally written in a similar form to this, but in Arabic:-
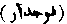 An officer of the Moghul Governemnt who was invested with the charge of the police, and jurisdiction in all criminal matters. A criminal judge. Faujdari is a term now used in British for a criminal suit as opposed to diwani, or civil.
An officer of the Moghul Governemnt who was invested with the charge of the police, and jurisdiction in all criminal matters. A criminal judge. Faujdari is a term now used in British for a criminal suit as opposed to diwani, or civil.
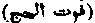 The end of the Pilgrimage. [PILGRIMAGE.]
The end of the Pilgrimage. [PILGRIMAGE.]
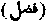 Lit. "That which remains over and above; redundant." A word used in the Qur'an for God's grace or kindness. Surah ii 244: "God is Lord of grace to men, but most men give no thanks." The Christian idea of divine grace, as in the New Testament, seems to be better expressed by fayz-I-aquas.
Lit. "That which remains over and above; redundant." A word used in the Qur'an for God's grace or kindness. Surah ii 244: "God is Lord of grace to men, but most men give no thanks." The Christian idea of divine grace, as in the New Testament, seems to be better expressed by fayz-I-aquas.
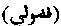 Lit. "That which is in excess." A term used in Muhammadan law for anything unauthorized, e.g. bai'-I-lazuli, is an unauthorized sale. Nikah-I-fazula is an unauthorized marriage, when the contracts are made by an unauthorized agent.
Lit. "That which is in excess." A term used in Muhammadan law for anything unauthorized, e.g. bai'-I-lazuli, is an unauthorized sale. Nikah-I-fazula is an unauthorized marriage, when the contracts are made by an unauthorized agent.
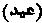 ; dual 'idan; plural a'yad. The two great festivals of the Muhammadans are, the 'Idu 'l-Fitr, and the 'Idu 'l-Azha. The other festivals which are celebrated as days of rejoicing are, the Shab-I-Barat, or the fifteenth day of Sha'ban; the Nau-Roz, or New Year's day; and Akhir-I-Chahar Shamba, or the last Wednesday of the month of Safar; the Laylatu 'r-Ragha'ib, or the first Friday in the month of the month Rajab; the Maulud, or the birthday of Muhammad.
; dual 'idan; plural a'yad. The two great festivals of the Muhammadans are, the 'Idu 'l-Fitr, and the 'Idu 'l-Azha. The other festivals which are celebrated as days of rejoicing are, the Shab-I-Barat, or the fifteenth day of Sha'ban; the Nau-Roz, or New Year's day; and Akhir-I-Chahar Shamba, or the last Wednesday of the month of Safar; the Laylatu 'r-Ragha'ib, or the first Friday in the month of the month Rajab; the Maulud, or the birthday of Muhammad.
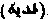 A ransom. From fida', "to ransom," "to exchange." An expiation
A ransom. From fida', "to ransom," "to exchange." An expiation
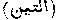 The title of the xcvth Surah of the Qur'an, so called because Muhammad makes the Almighty swear by that fruit in the first verse. Al-Baizawi says that God swears by the figs because of their great use. They are most excellent because they can be eaten at once, having no stones, they are easy of digestion, and help to carry off the phlegm, the gravel in the kidneys or bladder, and remove obstructions of the liver, and also cure piles and gout. (Tafsiru 'l-Baizawi, in loco)
The title of the xcvth Surah of the Qur'an, so called because Muhammad makes the Almighty swear by that fruit in the first verse. Al-Baizawi says that God swears by the figs because of their great use. They are most excellent because they can be eaten at once, having no stones, they are easy of digestion, and help to carry off the phlegm, the gravel in the kidneys or bladder, and remove obstructions of the liver, and also cure piles and gout. (Tafsiru 'l-Baizawi, in loco)
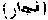 Lit. "That which is unlawful." A term given to a series of sacrilegious wars carried on between the Quraish and the Banu Hawazin when Muhammad was a youth, about A.D. 580-590. (Muir, vol ii 3)
Lit. "That which is unlawful." A term given to a series of sacrilegious wars carried on between the Quraish and the Banu Hawazin when Muhammad was a youth, about A.D. 580-590. (Muir, vol ii 3)
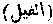 The title of the cvth Surah of the Qur'an, as it gives an account of the Ashabu 'l-Fil, or "People of the Elephant." [ELEPHANT.]
The title of the cvth Surah of the Qur'an, as it gives an account of the Ashabu 'l-Fil, or "People of the Elephant." [ELEPHANT.]
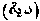 . A term which, in its strictest sense, means a sum exacted for any offence upon which the person, in consideration for the claim of qisas, or retaliation, not being insisted upon. (This does not apply to willful murder.) A full and complete line is that levied upon a person for manslaughter, which consists of either one hundred female camels or ten thousand dirhams (silver), or one thousand dinar (gold).
. A term which, in its strictest sense, means a sum exacted for any offence upon which the person, in consideration for the claim of qisas, or retaliation, not being insisted upon. (This does not apply to willful murder.) A full and complete line is that levied upon a person for manslaughter, which consists of either one hundred female camels or ten thousand dirhams (silver), or one thousand dinar (gold).
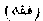 The dogmatic theology of the Muslims. Works on Muhammadan law, whether civil or religious. The books most read by the Sunnis are the Hidayah, written by a learned man named 'Ali ibn Abi Bakr, A.H. 593, part of which has been translated by the late Colonel, Charles Hamilton; the Darru 'l-Mukhtar, by 'Ala'o 'd-din, A.H. 1088; the Sharhu 'l-Wiqayah, by Ubaidu 'llah ibn Masud, A.H. 745; the Raddu 'l Muhtat by Saiyid Muhammad Amin ibn Abidi 'd-din, and the Fatawa 'Alamgiri. Amongst the Imamiyah School, or Shi'ahs, the principal works are Kitabu 'sh-Sharai', by Abu 'l-Hasan 'Ali (A.H. 326); the Muqni' f i'i Fiqh by Abu Ja'far (A.H. 360); the Shara i'u 'l-Islam, by Shaikh Najmu d-din (A.H. 679); and the Jami'u 'l-Abbasi, by Baha'u d-din (A.H. 1031).
The dogmatic theology of the Muslims. Works on Muhammadan law, whether civil or religious. The books most read by the Sunnis are the Hidayah, written by a learned man named 'Ali ibn Abi Bakr, A.H. 593, part of which has been translated by the late Colonel, Charles Hamilton; the Darru 'l-Mukhtar, by 'Ala'o 'd-din, A.H. 1088; the Sharhu 'l-Wiqayah, by Ubaidu 'llah ibn Masud, A.H. 745; the Raddu 'l Muhtat by Saiyid Muhammad Amin ibn Abidi 'd-din, and the Fatawa 'Alamgiri. Amongst the Imamiyah School, or Shi'ahs, the principal works are Kitabu 'sh-Sharai', by Abu 'l-Hasan 'Ali (A.H. 326); the Muqni' f i'i Fiqh by Abu Ja'far (A.H. 360); the Shara i'u 'l-Islam, by Shaikh Najmu d-din (A.H. 679); and the Jami'u 'l-Abbasi, by Baha'u d-din (A.H. 1031).
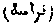 , or farasah. A Sufi term for the enlightenment of the heart. A penetration into the secrets of the unknown. 'Ilmu 'l-firasak. "The science of physiognomy."
, or farasah. A Sufi term for the enlightenment of the heart. A penetration into the secrets of the unknown. 'Ilmu 'l-firasak. "The science of physiognomy."
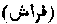 . Lit. "A couch." In Muhammadan law "a wife."
. Lit. "A couch." In Muhammadan law "a wife."
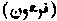 . [PHAROAH.]
. [PHAROAH.]
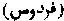 . The highest stage of celestial bliss. [PARADISE.]
. The highest stage of celestial bliss. [PARADISE.]
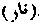 (1) The term an nar, "the fire", is generally used in the Qur'an and the Traditions for "hell." (2) In the Qur'an (Surah xxxvii 29) the power of God is declared as being able to give fire out of a given tree." On which al Bazizawi says :the usual way of getting fire is by rubbing two pieces of wood together one of which is markh and the other afar, and they produce fire, although both the sticks are green. (3) The burning to death of human beings is condemned by Muhammad, who said 'Let no one punish with the punishment of fire but God'.
(1) The term an nar, "the fire", is generally used in the Qur'an and the Traditions for "hell." (2) In the Qur'an (Surah xxxvii 29) the power of God is declared as being able to give fire out of a given tree." On which al Bazizawi says :the usual way of getting fire is by rubbing two pieces of wood together one of which is markh and the other afar, and they produce fire, although both the sticks are green. (3) The burning to death of human beings is condemned by Muhammad, who said 'Let no one punish with the punishment of fire but God'.
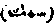 (1) Fish which, dying of themselves float upon the surface of the water are abominated, according to Abu Hanifah. Ash Shaf'i and Malik say they are indifferent. Abu Hanifah teaches that fish which are killed by accident are lawful but such as die of themselves without any accident are unlawful. There are, however, different opinions regarding those which die of extreme heat or cold.
(1) Fish which, dying of themselves float upon the surface of the water are abominated, according to Abu Hanifah. Ash Shaf'i and Malik say they are indifferent. Abu Hanifah teaches that fish which are killed by accident are lawful but such as die of themselves without any accident are unlawful. There are, however, different opinions regarding those which die of extreme heat or cold.
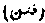 pl. of fitnah. Seditions; strifes; commotions.
pl. of fitnah. Seditions; strifes; commotions.
 Lit. "Nature." Certain ancient
practices of the prophets before the time of Muhammad which have not been forbidden
by him.
Lit. "Nature." Certain ancient
practices of the prophets before the time of Muhammad which have not been forbidden
by him.
 According to Muhammadan writers, there are five external (zahari) sense and five internal
According to Muhammadan writers, there are five external (zahari) sense and five internal
 pl. ataimah. The injunctions contained in the Qur'an (Surah ii, 167) respecting food are as follows: "O ye who believe! Eat of the food things with which we have supplied you, and give God thanks if ye are His worshipers. Only that which dieth of itself, and blood, and swine's flesh, and that over which any other name than that of God hath been invoked, hath God forbidden you. But he who shall partake of them by constraint, without desire, nor of necessity, then no sin shall be upon him. Verily God is forgiving and merciful." Surah v 92: "O Believers! Wine (khamr) and games of chance, and statues, and divining arrows are only an abomination of Satan's work! Avoid them that ye may prosper."
pl. ataimah. The injunctions contained in the Qur'an (Surah ii, 167) respecting food are as follows: "O ye who believe! Eat of the food things with which we have supplied you, and give God thanks if ye are His worshipers. Only that which dieth of itself, and blood, and swine's flesh, and that over which any other name than that of God hath been invoked, hath God forbidden you. But he who shall partake of them by constraint, without desire, nor of necessity, then no sin shall be upon him. Verily God is forgiving and merciful." Surah v 92: "O Believers! Wine (khamr) and games of chance, and statues, and divining arrows are only an abomination of Satan's work! Avoid them that ye may prosper."
 . The word zina'
includes both fornication with an unmarried person and adultery with a married person.
[ADULTERY.]
. The word zina'
includes both fornication with an unmarried person and adultery with a married person.
[ADULTERY.]
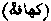 . Mu'awiyab ibn Hakam relates that he asked the Prophet if it were right to consult fortune-tellers about future events, and he replied, "Since you have embraced Islam, you must not consult them. [MAGIC.]
. Mu'awiyab ibn Hakam relates that he asked the Prophet if it were right to consult fortune-tellers about future events, and he replied, "Since you have embraced Islam, you must not consult them. [MAGIC.]
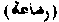 . According to Abu Hanifah, the period of fosterage is thirty months but the two disciples, Yusuf and Muhammad, hold it to be two years, whilst Zufar maintains that it is three years. Fosterage with respect to the prohibitions attached to it is of two kinds: first, where a woman takes a strange child to nurse, by which all future matrimonial connection between that child and the woman, or her relations within the prohibited decrees, is rendered illegal; secondly, where a woman nurses two children, male and female, upon the same milk, which prohibits any future matrimonial connection between them. For further particulars on this subject, see Hamilton's Hidayah, vol I, page 187.
. According to Abu Hanifah, the period of fosterage is thirty months but the two disciples, Yusuf and Muhammad, hold it to be two years, whilst Zufar maintains that it is three years. Fosterage with respect to the prohibitions attached to it is of two kinds: first, where a woman takes a strange child to nurse, by which all future matrimonial connection between that child and the woman, or her relations within the prohibited decrees, is rendered illegal; secondly, where a woman nurses two children, male and female, upon the same milk, which prohibits any future matrimonial connection between them. For further particulars on this subject, see Hamilton's Hidayah, vol I, page 187.
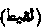 . Lit. "That which is picked up." The person who finds the child is called the multaqit. The taking up of a foundling is said to be a laudable and generous act, and where the finder sees that the child's life is in peril, it is an incumbent religious duty. (Hidayah, vol ii p 252)
. Lit. "That which is picked up." The person who finds the child is called the multaqit. The taking up of a foundling is said to be a laudable and generous act, and where the finder sees that the child's life is in peril, it is an incumbent religious duty. (Hidayah, vol ii p 252)
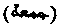 "The Day of Assembly." The Muhammadan Sabbath, on which they assemble in the Jami Masjid, or chief mosque, and recite two rik'ahs or prayers and listen to the oration, or khutbah at the time of mid-day prayer. Muhammad claims in the Traditions to have established Friday as the day of worship by divine command. He says, "Friday was ordered as a divine day of worship both for the Jew and Christian, but they have acted contrary to the command. The Jew fixed Saturday and the Christian fixed Sunday."
"The Day of Assembly." The Muhammadan Sabbath, on which they assemble in the Jami Masjid, or chief mosque, and recite two rik'ahs or prayers and listen to the oration, or khutbah at the time of mid-day prayer. Muhammad claims in the Traditions to have established Friday as the day of worship by divine command. He says, "Friday was ordered as a divine day of worship both for the Jew and Christian, but they have acted contrary to the command. The Jew fixed Saturday and the Christian fixed Sunday."
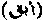 . The capture of a fugitive slave is a laudable act, and the captor is entitled to a reward of forty dirhams. (2) A fugitive on account of religion is called muhajir
. The capture of a fugitive slave is a laudable act, and the captor is entitled to a reward of forty dirhams. (2) A fugitive on account of religion is called muhajir 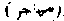 . Special blessings are promised on those who flee their country on account of their being Muslims.
. Special blessings are promised on those who flee their country on account of their being Muslims.
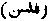 An idol (or an idol temple), belonging to the Bani Taly, a tribe divided between the profession of idolatry and Christianity. Destroyed by Ail by order of Muhammad, A.H. 630. (Muir, vol iv p 177.)
An idol (or an idol temple), belonging to the Bani Taly, a tribe divided between the profession of idolatry and Christianity. Destroyed by Ail by order of Muhammad, A.H. 630. (Muir, vol iv p 177.)
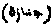 [BURIAL.]
[BURIAL.]
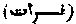 The river Euphrates, said to be one of the rivers of Eden. [EDEN.]
The river Euphrates, said to be one of the rivers of Eden. [EDEN.]
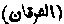 (1) The title of the xxvth Surah of the Qur'an. (2) One of the titles of the Qur'an (Surah ii 181; iii 2; xxv 1). (3) The title given to the Taurat revealed to Moses (Surah ii 50; xxi 49). (4) The victory on the day of the battle of Badr (Surah viii 42) (5) A terms used by Sufi mystics for a distinguishing between truth and error.
(1) The title of the xxvth Surah of the Qur'an. (2) One of the titles of the Qur'an (Surah ii 181; iii 2; xxv 1). (3) The title given to the Taurat revealed to Moses (Surah ii 50; xxi 49). (4) The victory on the day of the battle of Badr (Surah viii 42) (5) A terms used by Sufi mystics for a distinguishing between truth and error.
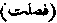 Lit. "Were made plain." A title of the xlist Surah of the Qur'an from the word occurring in the second verse. The Surah is also known as the Hamim as-Sajdah to distinguish it from the Surah xxxiind, which is also called as-Sajdah, or "Adoration."
Lit. "Were made plain." A title of the xlist Surah of the Qur'an from the word occurring in the second verse. The Surah is also known as the Hamim as-Sajdah to distinguish it from the Surah xxxiind, which is also called as-Sajdah, or "Adoration."